Ever since the dawn of civilization, human interest in land has been to produce food, fibre, fuel and timber. Land and society have always had an intimate relationship. Land resources constitute the fundamental base of all human beings. It is a priceless resource and is quite important to every individual and every nation. The way and extent to which this natural resource is utilized set the pace of a nation’s economic development. Unfortunately, land is getting scarcer and scarcer with each passing day, firstly, because of the burgeoning population and secondly, because of the merciless manner in which it is being used or rather abused.
The land resource is finite, with increasing human population, the per capita land is decreasing rapidly. And so, management of land and soil calls for dynamic management initiatives to ensure food security, nutritional security, environmental safety, and improved quality of life. The terminologies “land and soil” are interchangeable as far as its ultimate relationship with society is concerned. We need to develop awareness about these precious resources so that we can preserve them. In this unit, we shall focus on land use or land cover. Land is a finite resource and various sectors compete for its allocation. Therefore, the proper use of land according to its land capability could only lead to best outputs.
LAND ANS SOIL: Although land and soil are closely related yet the two are different entities. Land is a two-dimensional entity representing geographical area and the landscape. The land resource is composed of “Soil System” along with its natural functions providing the topographic features of the landscape. Soil is a three dimensional body with length, breadth and depth. Soil is in fact a living entity and a soil profile with well marked horizons tells the history of its formation and bears the imprint of many physical, chemical and biological processes which have led to its present form. The upper and bio-chemically weathered portion of the regolith is called soil. So, Soil may be defined as “ a collection of natural bodies which have been synthesized in profile form from a variable mixture of broken and weathered minerals and decaying organic matter, which covers the earth in a thin layer and which supplies, when containing the proper amounts of air and water, mechanical support and sustenance for plant.”
For all practical purposes soil is a non-renewable resource in a human life span. Land use and land cover is not static. Land use is dynamic and changes both in short-term and in long-term as well as spatially. The development in technology, increasing needs of the rising population, anticipated climatic changes, fast changing social values and new economic regimes are bringing about rapid changes in the land use pattern. Land use is product of physical environment and social and technological framework of a given society. Thus, for planning, the present and future land use, a set of biophysical and social-economic variables need to be studied.
The concept of land use, is that, land use is a comparatively new branch of economic geography. It is intimately related with demand for a particular land use. Land use studies involve principles, techniques, controlling factors, classification, capability assessment and measurement, resource appraisal, conservation, land reforms and planning of land use. The terms land use and land utilization are generally used synonymously, although there are some fine differences between them. Land use capability is another term used which connotes potential capacity of a given tract of land to support different types of land utilization under some conditions such as understand the drivers of land use change, measure and forecast land use change etc.
The superiority of demand should be the first principle of the utilization of land. Physical form of the land should be recognized while planning land use. Maintenance of ecological balance should be kept in view. Natural environment is a powerful force in determining the land use and concentration of population over a piece of land. These are some of the principles of land use.
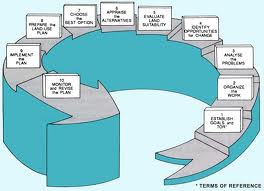
Land use planning is not recent in its origin but its practice is truly recent. The ultimate goal of land use study is to prepare plans for change in the present land use for betterment or to utilize the available land by the society in a different manner. A land use map gives a clear picture of land for deciding its future use. Beside land use productions potential, land use possesses human value and satisfaction of human needs is a vital concern. Reasonable share of agricultural land in urbanization, infrastructure development, recreation, growth of utility services and industries would be vital in planning the land use. Any future use of the land should satisfy the three basic needs of the people, e.g., food, shelter and clothing while maintaining the potential of the resource. Land use planning as related to agriculture should not merely be the rational use of land put to cultivation and/or bringing more land area under the plough, but should include conservation of resource from erosion, resource health and application of modern technology. Besides what is stated, scientific and rational land use planning should ensure ecological balance and proper equilibrium between the environment and the socio-economic needs of the people of the area.



Leave a Reply