To protect the environment from degradation by human activities, it is necessary to enforce environmental laws. The legal control for the protection of environment was incorporated by the 42nd amendment Act 1976 into the constitution.

The amendment act incorporated two new articles, Article 48A, and Article 51A(g). Article 48Asays that the state would protect and improve the quality of the environment where as Article 51A(g) says that it is the fundamental duty of every citizen to protect the environment including, lakes, rivers, wild life etc. The three important environmental laws in environmental history are : The Water Act(1974), The Air Act (1981) and the Environmental Protection Act (EPA Act. 1986).
The Water (Prevention and control of Pollution) Act, 1974

This act enacted by the parliament in 1974 for preventing and abating water pollution. Under this act, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) was constituted to promote cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the states. The CPCB was authorised to discharge the following functions:
• Advise the Central government on any matter pertaining to prevention and control of water pollution.
• Co-ordinate the activities of the State Pollution Control Boards and resolve dispute among them.
• Carry out and sponsor investigations and research relating to prevention/ causes of water pollution.
• Plan and organise training of persons to be engaged in programs for the prevention, control and abatement of water pollution.
• Organise comprehensive program through mass media regarding prevention and control of water pollution.
• Collect, compile and publish technical and statistical data relating to water pollution and the measures devised for its effective prevention and control.
• Prepare manuals, codes, or guides relating to treatment and disposal of sewage and trade effluents.
• Lay down, modify, or annual the standards for stream or well for the quality of water
• Establish or recognise a laboratory for analysis of samples of water or sewage.
• Plan a comprehensive program for the prevention, control or abatement of pollution of streams and wells in the state.
• Collaborate with CPCB for training of personnel.
• Inspect sewage or trade effluents, works, and plants for the treatment of sewage or trade effluents.
• Review plans, specifications or other data relating to setting up of sewage treatment plants , water treatment plants etc.
• Lay down standards for sewage and trade effluents and for the quality of waters form the discharge of effluents.
• Evolve economical and reliable methods of treatment of sewage and trade effluents.
• Evolve methods of utilisation of sewage and suitable trade effluents in agriculture.
• Evolve efficient methods of disposal of sewage and trade effluents on land.
The Air Act

The Air (prevention and control of pollution) Act was enacted by the parliament in 1981 for the prevention, control and abatement of air pollution. It entrusts the power of enforcing this act to the central as well as the State Pollution Control Boards.
Functions of the Central pollution control board (CPCB)
The Central Pollution Control Board performs the following functions, which each citizen must keep in mind and record, whether the board obeys these:
1. Advise the central government on matter concerning the improvement of the quality of air and the prevention, control or abatement of air pollution
2. Plan and cause to be executed for a nationwide program for the prevention, control or abatement of air pollution.
3. Co-ordinate the activities of the state and resolve the disputes among them.
4. Provide technical assistance and guidance to the State boards. Carry out and sponsor investigations and research relating to problems of air pollution.
5. Lay down the standards for the quality of air.
6. Collect, compile and publish technical and statistical data relating to air pollution and provide methods for its effective prevention, control or abatement- and prepare manuals, codes or guides relating to it.
The Environmental Act. 1986
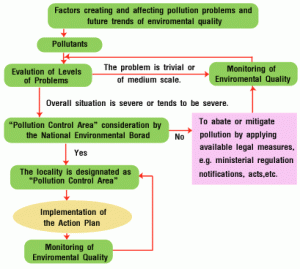
This was enacted by the parliament in 1986 to protect and improve the environmental quality, control and reduce pollution from all sources and prohibit or restrict the setting and/ or operation of any industrial facility on environmental grounds.
Powers of the Central Government to take measures to protect and improve environmental are mentioned as under:
1. Co-ordination of actions by the State Government
2. Planning and execution of nationwide program for prevention, control and abatement of environmental pollution
3. Laying down standards for the quality of environment in its various aspects
4. Laying down standards for emission or discharge of environmental pollutants from various sources
Some of the important aspects of this act are given below:
• Persons carrying on industry, operation of process cannot discharge any environmental pollutants in excess of prescribed standards.
• Persons handling hazardous substances shall have to comply with the safeguards prescribed under the following rules:
a) Hazardous wastes (management and Handling) Rules, 1986
b) Manufacture, storage and usage of hazardous Chemical Rules, 1989
c) Rules for manufacture, use, import, export, and storage of Hazardous Micro-organisms, genetically required organisms or cells.

Leave a Reply