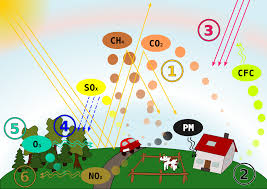
Air pollution is defined as the introduction of biological molecules, particulates or any other harmful materials into the atmosphere which will cause disease or even death to human being, cause damage to other living organism, affect the crops, and even buildings. The atmosphere is a natural gaseous system which is essential for life on earth. Ozone layer depletion is a known threat which is also caused by Air Pollution. The two of the world’s most toxic pollutions are Indoor air pollution and urban air pollution. According to a study, air pollution has caused a whooping 7 million deaths in the world. The chemicals in the air can be of natural means or manmade. The maximum amount of the pollutant in the air is due to man factor. The pollutants are classified into primary pollutants and secondary pollutants. The primary pollutants are pollutants that are emitted into the atmosphere directly, like the ash from the volcanic eruption, carbon monoxide from the motor vehicles, sulfur dioxide from the factories etc. While the secondary pollutants are not emitted directly, while they are the result of the primary pollutants. When the primary pollutants react or interact with the air, they form into a pollutant. Ground level ozone is an example of secondary pollutant, but any way they are caused by primary pollutants, so if there is a control of primary pollutant, then the air pollution can be reduced to a certain extent.

Here are some of the pollutants that are emitted into the atmosphere by human means,
- Sulphur oxides – Sulphur oxides are released into the atmosphere by volcanic eruptions, by industrial means, coal and petroleum has sulphur in it and their combustion causes sulphur dioxide. The oxidation of sulphur causes acid rain. The fuel power source is causing in the emission of sulphur into the air.
- Nitrogen Oxides – The nitrogen oxides are caused due to high temperature combustion and during the thunderstorm. It is one of the major pollutants and is brownish in color.
- Carbon monoxide – it is a very irritating gas and is caused due to incomplete combustion of wood, natural gas or coal. Vehicle exhaust also releases carbon monoxide.
- Volatile organic compounds – They are well known outdoor air pollutants. If they contain methane, it will result in global warming and the NMVOC’s will cause leukemia.
- Particulates – They are small, tiny particles which will fly with the air or gases. Some occur naturally from the volcanoes, forest fires, dust storms, sea spray etc, while some occur due to man efforts like, burning of fusel fuels, from industries, power plants. If the particulate become more, they can cause heart disease lung cancer and altered lung function.
- Persistent free radicals – They are airborne tiny particles and are tend to cause cardiopulmonary disease. Toxic metals such as lead and mercury are some of their compounds.
- CFC’s (Chlorofluorocarbons) – This is very harmful to the ozone layer and is emitted from the products which are banned now. The CFC’s when released into the air will rise to the stratosphere, and they combine with other gases and damage the ozone layer. This will allow the UV rays to reach the earth surface, which will cause skin cancer, eye diseases and damage to plants.
- Ammonia – This gas is emitted from the agricultural possesses. This gas has a pungent odor. The ammonia reacts with the secondary particles and form into oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
- Odors – they are from the garbage, sewage and industrial processes.
- Radioactive pollutants – These are produced by nuclear explosion, war explosives, nuclear events, and radioactive decay which is a natural process.
The secondary pollutants include smog, ground level ozone, Peroxyacetyl nitrate, organic pollutants. The sources of air pollution are,
- Stationary sources – from power plants, waste incinerators, manufacturing factories, other types of burning devices. While in developing countries, biomass is a major pollutant.
- Mobile sources – motor vehicles, marine vessels, air craft etc.
- Chemicals
- Fumes – from hair spray, paint, aerosol sprays, varnish etc.
- Waste depositions – Landfills, leading to the generation of methane.
- Military resources – nuclear weapons, toxic gases and rocketry.
Natural sources are,
- Dust from lands with no vegetation or buildings.
- Methane emitted from the digestion of food by animals.
- Radon from radioactive decay can affect the buildings and also can cause lung cancer.
- Smoke and carbon monoxide from wildfires.
- Volcanic eruptions.
The health effects of air pollution are,
- Mortality.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Lung disease.
- Cancer.
- Asthma, pneumonia and lower respiratory infections in children.
The air pollution is causing a lot of damage to the environment, if the control measures are not implemented fast, we will have to live in a surrounding with full of dust and non breathable gases. There are lot of air pollution control techniques and land use planning strategies. The land use planning involves zoning and transport and infrastructure planning. This should be implemented in many developing and under developing countries in order to control the air pollution.
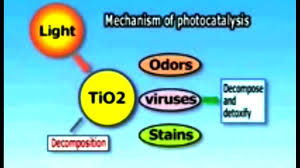
The use of electric vehicles should be used more in the place of petrol or diesel vehicles. Cleaner fuels can be used such as the bioethanol, bio diesel etc. The scientists have found a new gas to reduce the air pollution and that is Titanium dioxide which will break up those radicals, the VOC’s and NOx by emitting free electrons. A prof of University of Sheffield made a 10*20 meter poster which had Titanium dioxide, and was placed on a building roof so as to absorb the polluted air. This poster could absorb the pollutants from 20 cars each day.
The control devices are,
- Particulate controls are, Mechanical collectors, Electrostatic precipitators, Bag house, Particulate scrubbers.
- Scrubbers are, Baffle spray scrubber, Cyclonic spray scrubber, ejector venture scrubber, mechanically aided scrubber, spray tower, wet scrubber.
- NOx control devices are Low NOx burners, selective catalyst reduction, selective non-catalyst reduction, NOx scrubbers, Exhaust gas recirculation, and Catalytic converter.
- VOC abatement is Adsorption system, flares, thermal oxidizers, catalytic converters, bio filters, absorption, cryogenic condenser, vapor recovery system.
- Acid gas or Sulphur control, wet scrubbers, dry scrubbers, fuel-gas desulfurization.
- Mercury controls are Sorbent injection technology, Electro-catalytic oxidation, K-fuel.
Air pollution is a major havoc in future and if we don’t stop controlling it, we will have a huge task in front of us to clear off.

Leave a Reply