As we all know, trends in today’s marketplace, such as tight energy supplies, increasing energy prices, and the environmental impact of energy such as air pollution, are shining a spot light on energy economics. As social responsibility, climate change and green buildings become driving issues, leading businesses and institutions are looking to gain a competitive advantage by taking proactive steps to address these issues through effective energy management. Energy efficiency improvement is one of the prominent steps in this direction. Energy savings translate into financial value, which could be use to further develop energy resources and infrastructure.
Energy is necessary to run the buildings we work in and to make the products we use in our everyday lives. The energy uses in commercial buildings and manufacturing generates green house gases, but, it is possible to make significant reductions in these emissions cost-effectively. Here, we will learn various measures that can be take to improve energy services and infrastructure by improving energy efficiency on the supply as well as demand side.
Energy generation, transmission and distribution calls for the development of infrastructure. This not only involves capital outlays but also several other considerations such as public welfare and safety of the environment. In developing countries, energy infrastructures and facilities, critical decisions have to be taken to ensure stringent environmental standards and public good. First and foremost, the development of energy related facilities requires land and involves sound overall land-use planning but land such as that included in local conservation parks, areas reserved for ecological, scenic, geological or scientific value, coastal areas, habitats of various species, prime agriculture lands, etc must not include from consideration as sites for such facilities.
The development of large, energy related facilities should not proceed unless a definitive need for them has been demonstrated, through open public disclosure and certification of need, which cannot be met through conservation and smaller scale alternatives. Generating plants should be located as close as possible to load centres to avoid unnecessary corridors, for maximum efficient use of energy through utilization of waste heat for beneficial purposes, where the siting of a power plant conflicts with clean air goals, the emphasis should be placed on reducing the emissions of pollutants rather than relying on remote siting. The development of new electric corridors, as a great general principle, should be kept to an absolute minimum. In the development of such facilities, each level of government affected should be involved in the decisions to allow a balancing of national/regional and state/local energy and land use policy.
When considering a special specific facility, a full record should be developed in order that the least environmentally damaging alternative is selected. The decision should be made by an alternative board, independent commission set up in advance. The purpose of an energy system is to convert primary energy to useful or final energy. The energy efficiency level is balanced with the idea of cost efficiency, which implies that an energy-efficiency measures should be implemented only if it costs less than the least cost energy supply alternative. On the supply side of our energy systems, there is a very large potential for improving the efficiency of electricity generation by introducing new technologies that are more efficient than older power plants. The most advanced form of fossil fuelled power plant now available is the Combined Cycle Gas Turbine (CCGT). CCGTs are more than 50% efficient, compared with the older steam turbine, power plant that is still in wide spread use. They are more “climate friendly” than older, coal-fired steam turbine plant, because they burn natural gas, which on combustion emits about 40% less CO2 than coal per unit of energy generated.
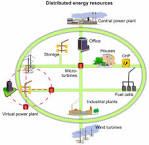
Improvement in the supply side efficiency of our electricity systems is possible by increasing the efficiency of generating plant and by ensuring that the “waste” heat is piped to where it can be used. Improving the sustainability of energy use by applying demand side measures involves two distinct approaches, one technological, and other social. Energy demand is usually broken down into three main sector: the domestic sector, the commercial and the institutional sector. Demand-side management handles changes as well as design of the technical energy system. Energy improving efficient appliances consumes less energy whilst delivering the same level of service as their inefficient predecessors. They have improved control systems, to ensure that energy consuming equipment is switched off when not needed, and that power output levels, match the requirements of users.
Apart from improving the energy efficiency of buildings and appliances, in industrial sectors, where the approaches are similar to those in the domestic and service sectors, there are other measures that apply specifically to industry. In particular these include cascading of energy uses, where waste heat from a high temperature process is used to provide energy for lower temperature process. High efficiency electric motors, pumps, fans and drive system are used with accurate matching of motors, to the tasks they are required to perform, and accurate sizing of pipes and their associated pumps. This calls for energy use optimisation of all possible levels by choosing the best suited energy practices vetted through effective energy simulation models.
Their is also another main technological measures that can be taken to conserve energy and use it more efficiently within buildings include- improved levels of insulation, energy-efficient windows, drought proofing and heat recovery systems, more efficient boilers, energy efficient lights Etc.+


Leave a Reply