Converting waste materials that are potentially useful into new products ,in order to reduce the energy usage , to prevent pollution ,to curb the release of greenhouse gases and also to prevent the waste disposal is called as recycling.
The mantra ‘ Reduce, Reuse and Recycle’ is indeed something that has acquired acute preponderance nowadays.

There are some ISO standards that pertain to recycling too .For environmental management control there is ISO 14001:2004 and for plastics there is ISO 15270:2008.
Basically, reusing any kind of biodegradable wastes is called recycling.
The waste materials are picked up from the streets or curbs and then they are correctly sorted and cleaned. These materials are then given for recycling or reprocessing.
Recycling would therefore produce products of the same kind. For instance, used paper would be converted into recycled paper.
There is another method of recycling too. It’s called the salvage method. Here, a particular material is extracted from an old, used material or in other words, it is recycled from a complex material. For instance, gold can be obtained from discarded computer components or lead from old car batteries.
This procedure of recycling can be done a number of times and eventually the material gets totally degraded and won’t be eligible for recycling further.

Raw materials required for recycling are called as recyclates .These recyclates are sent to a waste recycling plant where they are processed. These materials are then converted into new reusable products. For example, the plastic bottles are reprocessed to produce plastic pellets, which is a different product.
For a successful recycle, the quality of the recyclate has to be up to the mark. If the quality is not good, then the resulting recycled product will be apparently, down-cycled.
High-quality recycling does have numerous benefits. For example, it helps in augmenting the economy by producing products of higher economic value. Moreover, it does create a business and even customer confidence regarding the waste and resource management sector.
Recycling can be strategically done by sorting out plastic and paper materials in local drop-off centres. This will relieve the workers of an additional task of sorting out materials at the general waste streams when the people themselves throw the wastes in their respective locations.
The collection of wastes can be done by different methods. ‘Drop-off centres’, ‘curbside or street side collection’ or ‘ buy-back centres’ are some of them.
Drop-off centres:

This is one of the easiest and convenient types of waste collection where the waste producers themselves have to go to a central location where the recylates have to be sorted.
Street side collection:

Here, the wastes are gathered from different locations and they are normally in the mixed-waste form. The workers collect the wastes from the curb sides and a waste collection vehicle carries them to a central location where the wastes are sorted and given to a waste-recycling plant.
Buy-back centres:
In these centres, the wastes are purchased for an incentive. After processing the wastes in a waste-recycling plant, they are then sold with an expected profit.
Recycling of E-wastes:

With the accelerated rate of increase of the discarded e-wastes, recycling these has turned out to be a defying task. With the e-stewards certification, the e-waste recycling has been encouraged and recyclers are provided for the processing of these wastes.
Recycling of plastic wastes:
In this process, the discarded plastic products are strategically converted into useful products.
There can be two kinds of recycling here:
1) Physical:
Here the physical structure of the products is changed by melting the plastic products and converting them into useful products.
2) Chemical:
Here, the products/ polymers are converted into their monomers and then further converted back to the polymer form.
The Recycling codes:
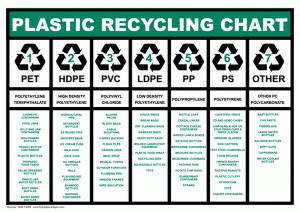
There are a number of codes that are followed in the process of recycling. The Society of the Plastics Industry first coded this chart in 1988.
Based on the types of resins that are present in plastic products they are numbered from one to seven. This is the resin coding system.
The plastic found in water bottles is numbered as 1. This is a PET type plastic. Type 2 is HDPE, hard plastic found in dishware. Type 3 is PVC that is normally found in shampoo bottles or credit cards. Type 4 is LDPE that is commonly found in tote bags and shopping bags .Type 5 is PP found in bottles, straws and the popular Tupperware too. Type 6 is PS found in compact disk cases. Type 7 includes all the rest which can range from bulletproof plastics to sunglasses.
There is a further negotiation too regarding the importance of recycling. The critics have clearly stated that the amount of energy and expenses incurred in recycling is much more than that in virgin production. Furthermore, the people who work under the manufacturing of virgin products are paid better than in jobs where recycling is involved. Hence, recycling doesn’t seem to be a better alternative for the workers as well.
Yet, recycling has indeed turned out to be of great use. This not only causes a reduction in wastes in our environment but also provides recycled products at a cheaper price too. We need to inculcate this habit of using recycled products so that we can at least curb the rising demand of virgin production. For example, students can use recycled paper books that are cheaper when compared to the conventional books.
When the environment is ours, why should we hesitate to protect it?
Leave a Reply